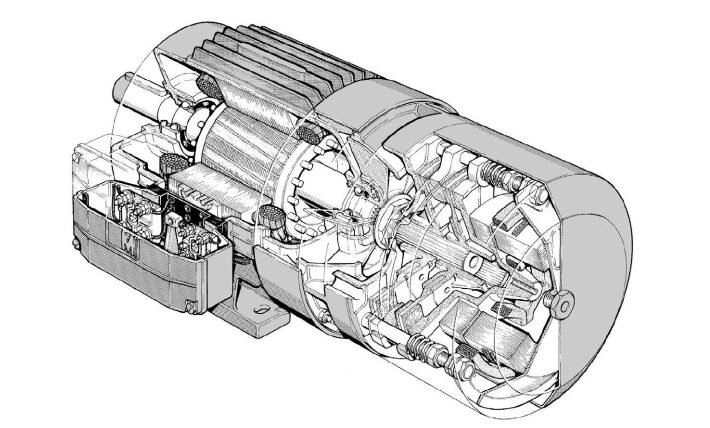
Comparison Between Asynchronous Motor and Brushless Motor
In the context of designing and managing electromechanical systems, choosing the right type of motor is a strategic decision. This article compares two widely used motor types: the asynchronous (induction) motor and the brushless motor, analyzing their main characteristics, advantages, disadvantages, and typical application areas. The discussion is intentionally simplified.
Asynchronous Motor
The asynchronous motor is an AC electric motor that operates through the generation of induced currents in the rotor caused by the stator’s magnetic field. It is the most commonly used motor in the industrial sector due to its simple construction and high reliability.
Main characteristics:
– AC power supply (typically three-phase
– Robust and standardized structure
– Requires an inverter for speed control
Advantages:
– Low cost
– Low maintenance
– Long life and high reliability
– Excellent for continuous operation
Disadvantages:
– Medium to high energy efficiency
– Less precise speed and torque control
– Larger size and weight compared to brushless motors
Typical applications:
– Industrial machinery movement, automated machines, pumps, fans, conveyors, compressor
Brushless Motor
The brushless motor is an electric motor without brushes, typically controlled by an electronic drive (ESC or inverter). It is suitable for contexts requiring high efficiency, fast dynamics, precision, and compact size.
Main characteristics:
– AC or DC power supply with electronic control
– High power density
– Low noise
Advantages:
– Higher energy efficiency
– Precise control of speed, torque, and position
– More compact and ligher
Disadvantages:
– Higher cost
– Requires complex control electronics
– Less rugged in harsh environments
Typical applications:
– Robotics, industrial automation, CNC machines, electric vehicles, medical devices
Direct Comparison
Comparison Table
| Characteristic | Asynchronous Motor | Brushless Motor |
| Cost | Low/medium | High |
| Efficiency | Medium-high | High |
| Control | Limited (with inverter) | Very precise |
| Maintenance | Minimal | Minimal |
| Noise | Medium (due to ventilation) | Low |
| Environmental Robustness | High | Medium |
| Size | Larger | Compact |
Conclusions
The choice between an asynchronous motor and a brushless motor strongly depends on the application. The asynchronous motor remains the ideal choice for standard industrial applications that require durability and continuous operation at low cost.
The brushless motor excels in contexts where efficiency, precision, dynamics, and compactness are essential.
It’s also important to note that the average efficiency of asynchronous motors has significantly improved with the implementation of the IEC 60034-30-1 standard.
Moreover, it is possible to precisely control the position and rotational speed of an asynchronous motor—making it similar to a brushless motor—by adopting a vector control architecture and integrating an encoder for feedback.
When evaluating the efficiency of a brushless motor, one must always consider the drive that powers it. Therefore, if torque or speed control is not required, the efficiency comparison with an asynchronous motor becomes very similar.


 Lun - Ven 8:00 - 17:00
Lun - Ven 8:00 - 17:00